Nature has a course of self-trimming, which means that it can take each plant and tree through an experience of a substantial shift in their living and growth. During the process, some plants may perish, others may survive; the plants that receive the least attention perish first.
Therefore, optimizing your garden and seeds for different seasons is crucial to help your plants to grow more healthily.
Whatever the season, you can always follow a few general strategies to improve your garden.
In this article, we’ll explore everything about those seasonal plants and optimizing tactics for your garden to ultimately achieve the lucrative cash crops.
Knowing your “USDA Zone”
Only learning about optimizing your garden and seeds for different seasons is not enough. You must check into the USDA zones more thoroughly.
So, what are USDA zones and their significance?
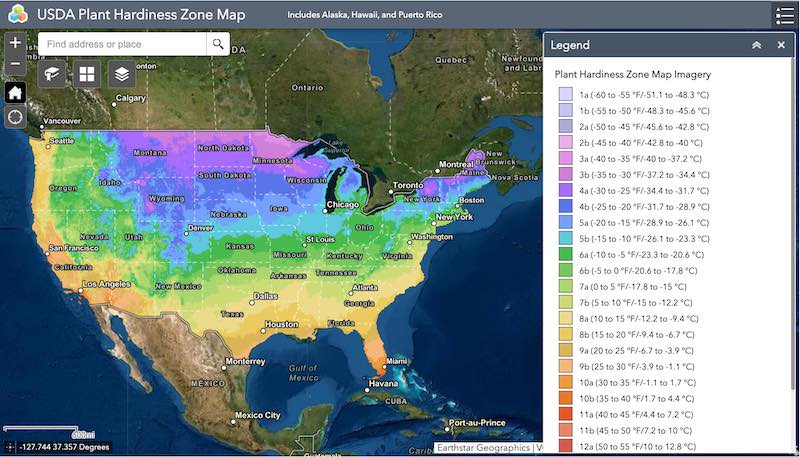
Put simply, the USDA Hardiness Zone Map is one of several maps created by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) to provide guidance to growers about which plants are likely to thrive in certain climates.
The map has, in total, 13 zones altogether in Canada and America, which are divided according to those regions’ average yearly lowest winter temperatures.
Each zone has a temperature difference of 10 degrees Fahrenheit; the lower the number, the colder the average lowest temperature is. So, to sum up, zone 1 has the coldest weather, while zone 13 has the warmest. Below is a detailed picture on the USDA Zone Map,
Now, what’s the best way to find out your USDA Zone? The easiest way is to use the USDA’s Plant Hardiness Zone Map. Simply input your zip code to see what zone you’re in.
Winter Garden
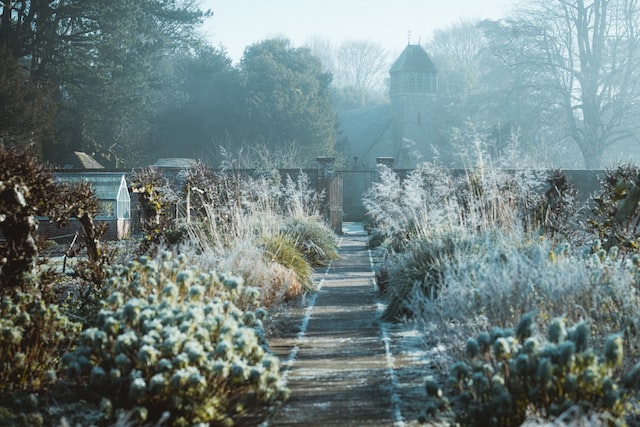

Although winter may seem like an off-season for gardening, a few cool-season vegetables grow best in winter. Besides, winter allows jump-starting the growing season by planting cold-hardy crops.
It would, therefore, be folly to ignore this cold season while planning your garden and seeds for different seasons.
However, much like every other garden, there are specific ways to optimize a winter garden as well. So, here are a few tips to optimize gardens in the early and late winter time,
Early winter
Clean up dead leaves and debris from your garden beds to prevent diseases and pests from overwintering your soil.
Once your beds are clean, add a thick layer of mulch to insulate the soil and protect your plants’ roots from freezing temperatures.
If tender plants need protection from the cold, consider constructing a simple greenhouse or cloche out of recycled materials like plastic bottles or milk jugs.
Finally, keep an eye on the forecast and take action if severe cold weather is predicted.
Late winter
Take a look at your plants and identify which ones require replacement. Once you know what to work with, you can start planning how to redecorate your garden with new seedlings.
Be sure also to fertilize and water the plants regularly. This is especially important if you live in an area that tends to be dry during this time of year.
Provide plenty of light and warmth for your seedlings. In that case, you may keep them in sunlight during the daytime.
The seeds to plant during winter
Plant seeds like kale, Swiss chard, English peas, radishes, carrots, and onions for winter season harvest. Also, look for other vegetables, such as Brussels sprouts, broccoli, and cauliflower.
You may also go with herb transplant seedlings if you are interested in harvesting a herb garden.
Spring Garden

Spring is a time of new growth, so optimizing your garden and seeds for the best results is essential. However, while both early and late spring benefits garden optimization, there are key differences that gardeners should be aware of,
Early spring
Starting early in the season can give your plants a longer growing season. This can result in more flowers and a more bountiful harvest come summer. However, knowing the risk of light frost damage to early blooms is essential.
Late spring
Waiting until later in the season to start your garden has the advantage of avoiding the risk of frost damage. However, you’ll need to be diligent about watering and fertilizing to compensate for the shorter growing season. So, the decision is entirely yours whether to go with early spring seedings or later ones.
The seeds to plant during spring
Most vegetables do well in cooler climates and can be planted in early spring. These plants may include peas, radishes, and spinach.
Nevertheless, as the weather warms up, you can plant more heat-loving crops like tomatoes, peppers, and eggplants. Herbs such as basil, chives, and cilantro can also be planted in the spring.
Summer Garden
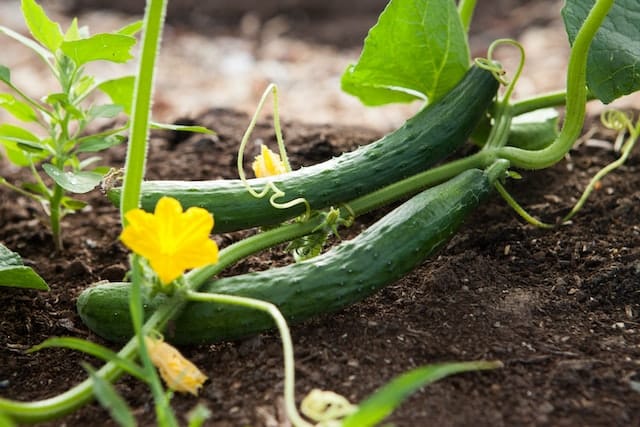

Different seasons call for different strategies in the garden. For example, you might concentrate on springtime seed-planting and burying them in the soil. But as the summer heat sets in, you might need to focus on ways to keep your plants cool and hydrated.
So, how do you prepare your garden for summer? Similar to other seasonal gardens, summer has to be optimized differently for the early and late periods. For instance,
Early summer
Cut back on watering. As the weather cools down, your plants will need less water. So, cut back on watering gradually over the next few weeks.
Fertilize lightly. Give your plants a light feeding of fertilizer to help them recover from the summer heat and to encourage new growth.
Late summer
Late summer is the perfect time to give your garden extra attention. So, focus on plants that will produce fruit in the fall.
Also, think about fall or autumn crops’ rotations. This is the time to start planning what you’ll plant in the fall to make the most of your garden space.
The seeds to plant during Summer
The best time to plant most annual flowers and vegetables is during the summer. The warm weather and long days help the plants grow quickly and produce a bountiful harvest.
Impatiens, cosmos, marigolds, and zinnias are among the best summer seeds to plant. Many vegetables do well when planted during summer as well, including tomatoes, peppers, eggplant, and squash.
Fall Garden
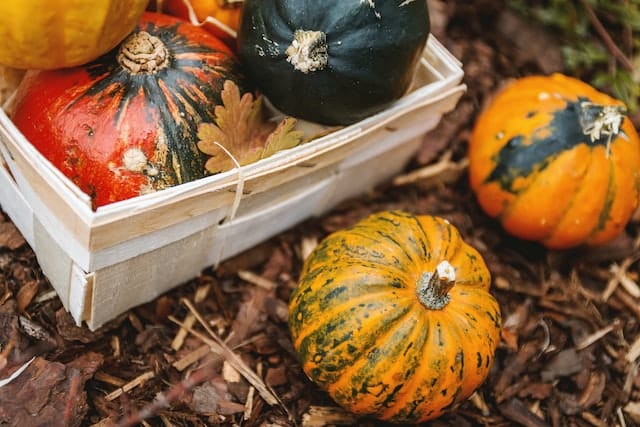

The autumn season, often known as fall, is ideal for preparing your garden for winter. But what is the most effective approach? Should you start early or wait until later in the season?
Well, there are benefits to starting early and waiting until later in the fall to optimize your garden. So, you should make seeding preparations for both.
Early fall
If you want your garden to be in peak condition for the fall, it’s important to start optimizing it early.
This means doing things like fertilizing regularly, ensuring the pH level is balanced and ensuring that all the other plants are watered regularly.
Late fall
Waiting until late fall to start optimizing your garden is not as effective. Also, you may find that your plants are already suffering when you start trying to improve their condition.
However, remember that it is never too late to start on anything. So, making last-minute preparations to prepare your garden for winter is also crucial during the late fall. This is also a good opportunity to start harvesting and storing your firewood if you’re growing firewood.
The seeds to plant during the fall
Some of the best seeds to plant during fall are Black-Eyed Susan, Aster, Pancy, Radish, Hollyhocks, Larkspur, Columbine, Poppies, Penstemon, Purple Coneflower, etc. Fall is also an excellent season to plant trees and bushes.
To Summarize
Optimizing your garden and seeds for different seasons might seem daunting at first, but with time, you will get it all in hand.
Just be informed, prepared, and choose the right seeds. Know the characteristics of various flowers, vegetables, herbs, fruits, and grasses. Learn more about them in-depth for building a more lively garden on your farm.
To help you get started, use the covered USDA zone variables, various seasonal traits, and the best seeds to plant at specific times of the year. These are sure to help you ensure a bountiful harvest year-round.
So, don’t let the changing seasons stop you from enjoying your hobby. Research more about your favorite plants and get to gardening ASAP!
Recommended reading:
Frequently Asked Questions about Plants & Seeds for Different Seasons
Different seasons offer different opportunities for planting. For example, it may be too cold in the winter to plant vegetable seeds, but it is an excellent time to plant cover crops to protect your soil.
On the other hand, Spring and Fall are the best times to plant bulbs and fall harvest vegetables, whereas Summer works great with annual trees.
The USDA zone in gardening is an area that the United States Department of Agriculture defines. It is a method that divides plants into groups based on how well they can resist cold temperatures.
The zones are based on minimum average temperatures, with Zone 1 being the coldest and Zone 11 being the warmest.
The best time to plant seeds is in the spring when the weather is warm and the days are getting longer. By doing this, the seeds have a chance to blossom into solid plants before the scorching summer heat appears. You can plant seeds in other seasons but may not have as much time to grow before the weather becomes too hot or cold.
In most regions, the winter garden should be planted in late summer or early fall. This timing allows the plants to become established before the first frost and ensures a bountiful harvest come winter.
Keep in mind, however, that some plants (such as peas and spinach) prefer cooler weather and can be planted even closer to winter.
It is recommended to plant seeds for the spring garden six to eight weeks before the last average frost date in your area. Remember that some seeds germinate more slowly than others. Consult a seed packet or gardening catalog for information about the seeds you have chosen.
Several vegetables can be seeded in the winter, including peas, carrots, turnips, and radishes. The key is to start the seeds indoors in a sunny location and transplant them outdoors once the weather warms up.
Winter vegetables need to withstand cold temperatures, so make sure to choose varieties that are known to be hardy. You can enjoy a bountiful harvest of winter vegetables with a bit of care and attention.
Some cool-weather favorites include kale, spinach, Brussels sprouts, and broccoli. Fall is also an excellent season to sow root crops such as carrots, beets, and turnips. These vegetables will thrive in cooler temperatures and shorter days of autumn.
Annuals, perennials, and vegetables are the ideal plants to grow in a summer garden. Plants known as annuals only last one season before dying. Plants with a lifespan of two years or longer are considered perennials. Plants that are farmed for their edible components are known as vegetables.

7 replies on “Optimizing Your Garden and Seeds for Different Seasons”
[…] Optimizing Your Garden & Seeds for Different Seasons […]
[…] Optimizing Your Garden and Seeds for Different Seasons […]
[…] Optimizing your Garden and Seeds for Different Seasons […]
[…] Optimizing your Garden and Seeds for the Different Seasons […]
[…] branches, and other organic matter into a fine mulch that you can use on the flower beds or over winter crops like kale, cabbage, and […]
[…] you are located near some farmland, then your honeybees will be responsible for pollinating many different types of crops which in turn helps to keep the food industry […]
[…] Specifically, these crop species don’t have any growing season that makes it possible for the farmers to harvest at any time of the year and count a better profit from […]