We are now living in an era of great progress and urbanization. Places that are previously remotely populated are now bustling districts with towering skyscrapers and multi-lane expressways.
As more people are adapting to the urban lifestyle, it is imperative that an abundant food source and healthy living can be sustained.
This is why urban farming has become a staple in urban households all around the globe. But what is the difference between traditional and urban farming?
There was a time when the only means of growing food was through large-scale farming. Acres of land are planted with crops and come harvest time, the goods are delivered and distributed to towns and cities.
But as the population grows and more areas become urbanized, alternative means of sourcing food must be formulated.
In the urban setting, there are a lot more factors to consider when sourcing food. There is the matter of limited space, inaccessibility to agricultural districts, carbon footprint, and water scarcity.
The need for a more sustainable way of producing food has paved the way for urban farming.
Compared to traditional farming, urban farming only requires a very small space, needs smaller quantities of water, and emits fewer greenhouse gasses.
Urban and Traditional Farming Explained
Until recently, traditional farming was the only major means of growing produce on a large scale basis.
Farmers grow crops on acres of land, using irrigation systems connected to lakes and rivers, and use pesticides and other medicine to ensure that the crops are protected against pests and diseases.
The major problem with this is that it often leads to deforestation, uses large amounts of water, and emits greenhouse gasses that contribute to global warming.
The use of pesticides and heavy equipment and machinery also contributes to the environmental burden traditional farming entails.
Urban farming is the means of growing food individually or as a collective, in an urban setting. It is set using limited resources while trying to minimize carbon footprint. There are several types of urban farming.
Community farms are small farms set up within the urban community that are usually maintained by everyone that lives within the community and benefits from its produce.
This type of urban farming improves camaraderie among neighbors and helps maintain clean fresh air, and most importantly, produces fresh, home-grown food.
Urban Farms are also becoming a more popular type of urban farming. These small farms set up within the vicinity ultimately supply local markets with their products and keep the soil and air healthy, while not emitting so many greenhouse gasses.
An aquaponic system is another cool way of doing urban farming. Aside from plants, it also involves fish. The system aims to create a sustainable ecosystem using both plants and fish by-products to thrive.
A hydroponic system is an urban farming method wherein plants are grown without the use of soil.
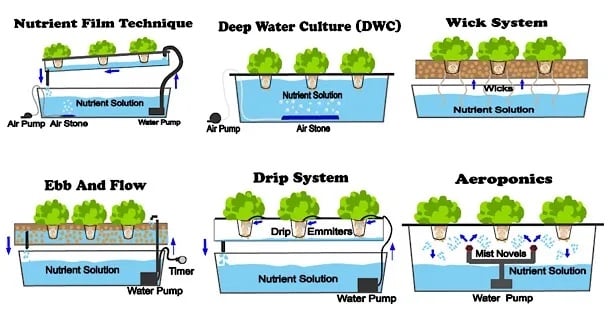
How Urban and Traditional Farming Differ
In terms of productivity, traditional farms win the traditional vs urban farming narrative.
Traditional farming usually caters to large-scale markets, thus the need for high productivity.
Machinery, techniques, and processes all focus on high output yield. Urban farming usually provides for families or small communities, so high productivity is not that sought after.

Space
Traditional farming needs a lot of space. Acres of land are used for various crops all year long.
Urban farming does not require large spaces. It can even be done in one’s own backyard!
Sustainability
Traditional farms use up a lot of resources to sustain their growth and productivity. Irrigation, pesticides, fertilizers, and acres of land are required to keep a traditional farm running smoothly.
Urban farming is sustainable with minimum resources and maintenance.
GHG Emissions
Greenhouse gasses are one of the major causes of climate change and we all need to limit its emission. Unfortunately, traditional farming is one of the major contributors to GHG emissions.
Urban farming emits way less GHG since its process is simplified, almost eliminating the carbon footprint entirely.
Seasonal Production
Traditional farms grow crops according to season. So during the off-season for some produce, farmlands lay waste and resources keep getting used up even without yield.
Urban farming does not depend on whether the product is in season or off-season. Harvest can be expected all year long and you can optimize for different seasons.
Water Usage
Traditional farms require a lot of water. Irrigation systems are built near rivers and lakes to meet the farms’ water requirements. Farms even follow rain patterns for planting crops due to the high resource requirement.
Urban farming does not need a lot of water resources to be sustainable. Water can even be reused and not affect the sustainability and production of the farm.
Pros and Cons of Urban Farming

Urban farming has its own advantages and disadvantages. Here are some of the perks and drawbacks of doing urban farming.
Pros of Urban Farming
- Doesn’t require much space – Anyone can set up their own urban farm because it would not take up a lot of space. An urban farm can be set up in the backyard, rooftop, or even inside the home.
- Yields organic produce – Urban farms are normally not sprayed with insecticides and antibiotics. It also does not come from GMOs. It yields crops that are grown naturally without synthetic additives, thus organic!
- No seasonal crop – An urban farm setup allows produce to be grown all year round. Temperature, environment, and other factors are subdued, so the crops can be grown any time of the year.
Cons of Urban Farming
- Crops are susceptible to destruction – Since crops are not sprayed with pesticides and antibiotics, it is always at risk of getting pests or sick.
- Soil needs to be replaced on a regular basis – Unless the setup is hydroponic, there is a need to replace the soil on a regular basis due to its exposure to urban contaminants such as pollution.
Pros and Cons of Traditional Farming

Traditional farming has been around for generations, but it has its own strengths and flaws. Here are some of the pros and cons of traditional farming.
Pros of Traditional Farming
- Produce high output – The traditional farming system is designed for maximum productivity. Various methods are used to ensure that the processes of planting, irrigation, and harvest are efficient.
- Jobs – Due to their large-scale operation, traditional farms require manpower. This helps people within the community find jobs and earn income for their families.
Cons of Traditional Farming
- Emit high amounts of GHG – Traditional farms are still the major source of greenhouse gas emission that causes climate change and global warming.
- Might not be healthy to eat – Due to insecticides, antibiotics, and other drugs applied to the crops, it might not be healthy for human consumption anymore.
- Deforestation and loss of habitat – Forests are often cleared to be converted to farmlands. This is because soil can only be used several times before being deemed unusable for farming. Deforestation leads to habitat loss for wildlife.
In Conclusion
Traditional farming has been here for generations, and it is still the major source of food for people all around the globe.
But the gradual urbanization of districts and the need for a lesser carbon footprint calls for an alternative means of farming.
Urban farming requires less space, fewer resources, and almost zero carbon footprints – the perfect alternative for urban communities to have a sustainable source of food.
FAQs about Traditional vs Urban Farming
Urban farming is cultivating food in or around a city, while traditional farming takes place in rural areas. Urban farming uses smaller plots of land for growing small-scale crops, whereas traditional farming requires vast areas to grow larger crops like wheat and corn.
Traditional farming involves manual labor and the use of simple tools, while modern farming relies on advanced technology and machinery. Modern farming also uses synthetic fertilizers and pesticides to increase yields, whereas traditional farming relies on natural methods for pest control and soil fertility.
The advantages of traditional farming include preserving cultural practices, producing organic food, and being more sustainable. Disadvantages include lower yields, limited access to markets, and vulnerability to weather and pests.
The advantages of urban farming include access to fresh produce, community building, and reduced food transportation costs. Disadvantages include limited space for growing crops, potential soil contamination, and zoning restrictions.

2 replies on “Differences between Traditional and Urban Farming”
[…] the right tractor can make a significant difference in the efficiency and productivity of your farm operations. However, with so many different options available on the market, it can be overwhelming to decide […]
[…] offer some great advantages to urban farmers who don’t have the space or resources for large-scale […]